Example communication using Tcl
This section shows simple communication with Application Server using Tcl command language. Tcl is a very simple scripting and command language.
For more information on Tcl, see
- Official website: http://tcl.tk/
- Windows binary distribution can be found here: https://www.magicsplat.com/tcl-installer/index.html
Other scripting environments, like Python, should be able to control Application Server in very similar fashion. The Tcl is chosen here for its simplicity to demonstrate control principles as it can getestablish communication using only few socket configuration commands.
Setting up Application Server communication in Tcl
Creating a socket on localhost port 51234:
% set so [socket localhost 51234]
sock000001F0932F2CB0
Configuring the socket buffering to line:
% fconfigure $so -buffering line
Defining a new command called sendcmd that writes content into the socket, reads and returns the response:
% proc sendcmd {so cmd} {puts $so $cmd;gets $so data; return $data}
Controlling Application Server from Tcl
We can now send commands to the Application Server and receive the responses:
% sendcmd $so {acq start}
ok;acq start;starting...
% sendcmd $so {acq stop}
ok;acq stop;stopped
Receiving information on object detections
The Application Server provides the second TCP/IP channel where object detections are announced. We open the second Tcl comand shell, create an async socket and define a call back function that would be executed, when any data arrives. In the callback, we print the data sent by Application Server to the standard output. If the socket is closed, we close the processing.
We can past the following code to the Tcl command shall:
proc readData {serverChannel} {
global end
set noOfChars [gets $serverChannel data]
if {$noOfChars!=-1} {
puts "read: $data"
}
if {[eof $serverChannel]} {
close $serverChannel
set end 1
}
}
set sd [socket -async localhost 51300]
fconfigure $sd -blocking 0
fileevent $sd readable [list readData $sd]
vwait end
The first part defines the callback function. Then the socket is created and configured as non-blocking. The event callback is set on the socket connecting our callback function.
Finally, we enter event loop using "variable wait" vwait command. It blocks the system processing events until the variable "end" is created.
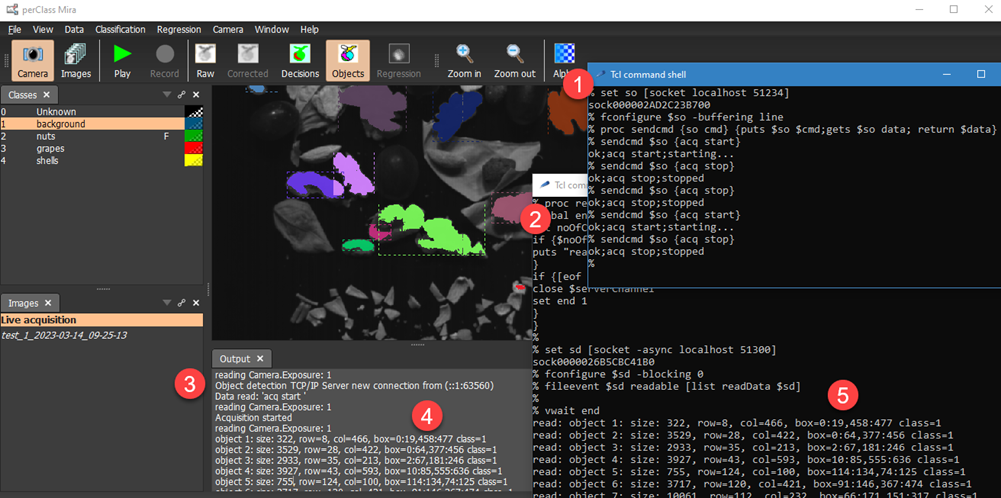
The complete application setup is shown in the following screenshot. Apart of the perClass Mira window, we have two separate shells (one Tcl shell  to issue commands and one shell receiving object detections
to issue commands and one shell receiving object detections ). .Once we connect in
). .Once we connect in  to the object detection channel on port 51300, perClass Mira Output window displays the connection details
to the object detection channel on port 51300, perClass Mira Output window displays the connection details . In the command shell
. In the command shell  , we can now start the acquisition using "acq start" command (note that also "acq info enable" cammand was run to enable object reporting and the display was set to show objects (not shown on the screenshot).
, we can now start the acquisition using "acq start" command (note that also "acq info enable" cammand was run to enable object reporting and the display was set to show objects (not shown on the screenshot).
As soon as the objects are detected in the live stream , the respective messages are sent over the object detection socket, captured in
, the respective messages are sent over the object detection socket, captured in  and printed to the standard output.
and printed to the standard output.